티스토리 뷰
LinkedList
ArrayList와는 하나의 큰 배열을 사용하는 방식이다.
이와는 다르게 LinkedList는 각각의 노드를 연결하는 방식을 사용한다.
연결 리스트로 구현되어 있고 각각의 데이터는 노드(Node)로 구성되어 연결되어 있는 구조다.
각 노드는 데이터와 다음 노드의 값을 가지고 있다.
LinkedList의 장점은 데이터 삽입/삭제가 용이하다는 점이다.
원하는 위치 어디에서나 삽입/삭제 시에 변경되는 노드만 다시 연결해주면 되기 때문에 빠른 연산이 가능하다.
LinkedList에서의 삽입 과정
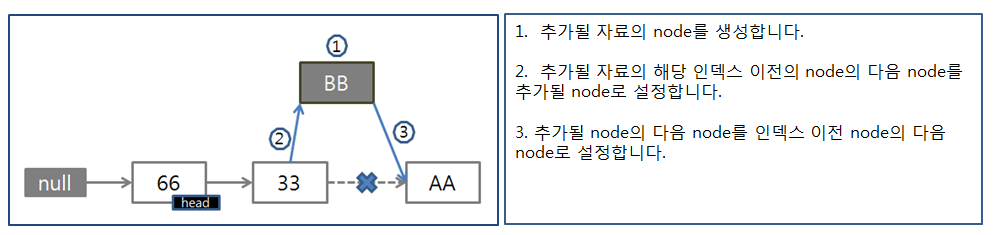
LinkedList에서의 삭제 과정

그래서 데이터의 삽입/삭제가 자주 발생하는 경우에 LinkedList를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
그러나, LinkedList는 순차접근만 가능하기 때문에 인덱스를 이용하여 자료를 검색하는 것에 적합하지 않다.
예를 들어, 5번째 데이터에 접근하기 위해서 바로 5번째 데이터에 접근할 수 있는 것이 아니라 첫번째 데이터부터 5번을 움직여서 검색해야 하기 때문이다. 즉, O(N)의 연산 속도가 걸린다.
이런 단점이 있기 때문에 데이터 검색이 빈번한 경우에는 ArrayList를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
JAVA로 직접 구현한 LinkedList
Node.class
package linkedList;
public class Node {
private Object data;
private Node next;
public Node() {
data = null;
next = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
LinkedList.class
package linkedList;
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
private int length;
public LinkedList() {
this.head = new Node();
this.length = 0;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
if(length<0) this.length = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return getLength() == 0;
}
public void add(Object data){
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.setData(data);
if(isEmpty()){
head.setNext(newNode);
}
else {
Node node = head;
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
node = node.getNext();
}
node.setNext(newNode);
}
setLength(length+1);
}
public void add(int index, Object data){
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.setData(data);
if(index == 0){
if(isEmpty()){
head.setNext(newNode);
}
else{
newNode.setNext(head.getNext());
head.setNext(newNode);
}
}
else{
if(index<0 || index>length) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
Node node = head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
node = node.getNext();
}
if(node.getNext() != null){
newNode.setNext(node.getNext());
node.setNext(newNode);
}
else {
node.setNext(newNode);
}
}
setLength(length+1);
}
public void remove(int index){
if(isEmpty()) System.out.println("삭제할 데이터가 없습니다.");
if(index>=length) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
Node node = head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
node = node.getNext();
}
node.setNext(node.getNext().getNext());
setLength(length-1);
}
public void print(){
if(isEmpty()) System.out.println("데이터가 없습니다.");
Node node = head.getNext();
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
if(node.getData() == null) break;
System.out.print(node.getData() + " -> ");
node = node.getNext();
}
System.out.println();
}
public boolean contains(Object data){
Node node = head;
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
node = node.getNext();
if(node.getData().equals(data)){
System.out.println("해당 데이터가 인덱스 " + i + "에 있습니다.");
return true;
}
}
System.out.println("해당 데이터가 없습니다.");
return false;
}
public Node getNode(int index){
Node node = head;
for(int i=0; i<=index; i++){
node = node.getNext();
}
return node;
}
}
Main.class
package linkedList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.add(0,2);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.add(2,0);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.remove(2);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.add(1,3);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.remove(1);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.remove(0);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.contains(1);
linkedList.contains(2);
System.out.println(linkedList.getNode(0));
System.out.println(linkedList.getNode(1));
}
}자바로 LinkedList를 구현해봤다. 우선 Node 클래스를 만들고 여러 개 노드로 이루어질 LinkedList를 구현했다.
위의 결과는 다음과 같다.

'Java > 개념정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] Queue (0) | 2021.09.23 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Stack (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| [Java] 데이터 타입, 변수, 배열 (0) | 2021.09.19 |
| [ Java ] JVM란? 자바의 실행 원리 알아보기 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| [ Spring ] Java 설정 파일 사용 및 설명 (@Configuration, @Bean, @EnableWebMvc) (0) | 2021.02.19 |
