티스토리 뷰
반응형
자바로 Queue를 직접 구현해봤다.
큐는 자료구조로, FIFO(First-in, First-out)의 특성을 가지고 있다.
두가지 방법을 사용해서 구현했다.
배열과 Node(연결 리스트) 방법 두가지다.
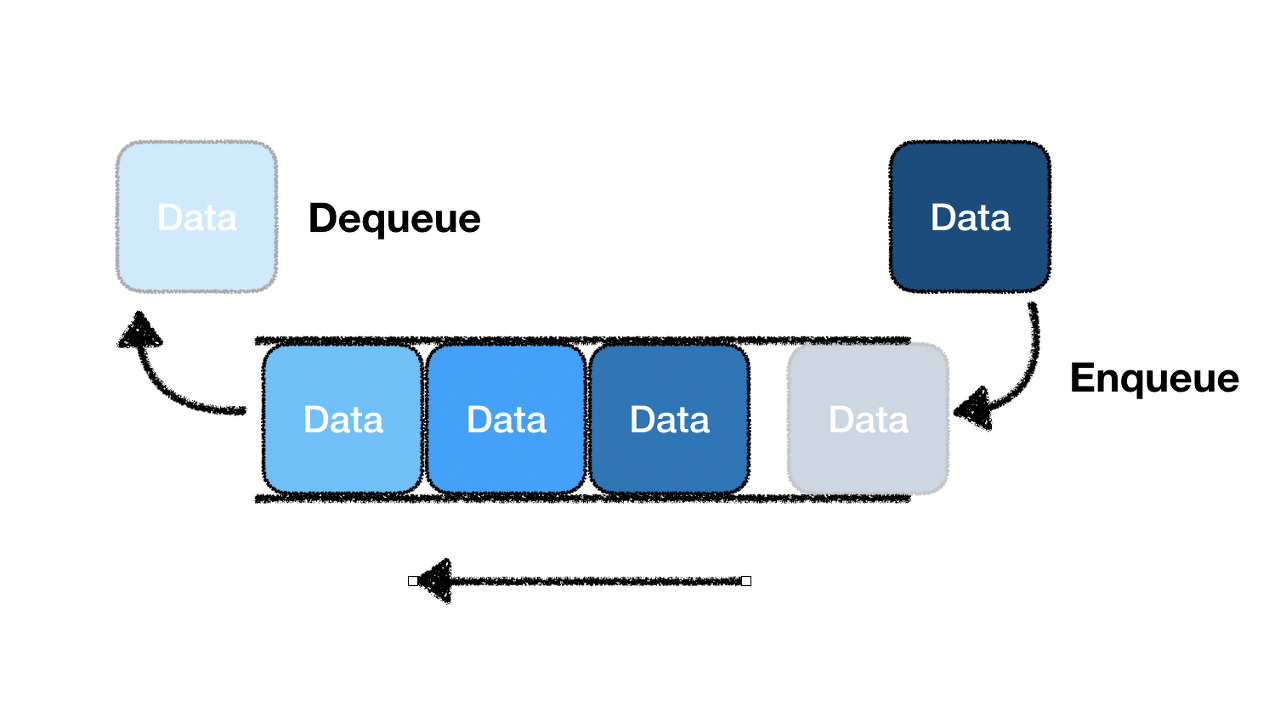
배열을 이용하여 구현
ArrayQueue.class
public class ArrayQueue {
private int[] arr;
private int size;
public ArrayQueue() {
arr = new int[20];
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;
if(size<0) this.size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public void add(int data){
arr[size] = data;
setSize(size+1);
}
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()) throw new NullPointerException();
int firstData = arr[0];
if(size > 1) {
for(int i=1; i<size; i++){
arr[i-1] = arr[i];
}
}
setSize(size-1);
return firstData;
}
}
Main.class
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//배열을 이용한 Queue
ArrayQueue arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue();
arrayQueue.add(1);
arrayQueue.poll();
arrayQueue.add(2);
arrayQueue.add(3);
arrayQueue.add(4);
while(!arrayQueue.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(arrayQueue.poll());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
결과는 다음과 같다.

Node를 이용하여 구현
배열과 다르게 각 노드가 연결되어 있는 구조이다.
Node.class
public class Node {
private Object data;
private Node next;
public Node() {
data = null;
next = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
NodeQueue.class
public class NodeQueue {
private Node head;
private Node node;
private int size;
public NodeQueue(){
head = new Node();
node = null;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;
if(size<0) this.size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.setData(data);
if(isEmpty()) {
head.setNext(newNode);
}
else{
node.setNext(newNode);
}
node = newNode;
setSize(size+1);
}
public Node poll(){
if(isEmpty()) throw new NullPointerException();
Node firstNode = head.getNext();
head.setNext(firstNode.getNext());
setSize(size-1);
return firstNode;
}
}
Main.class
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Node를 이용한 Queue
NodeQueue nodeQueue = new NodeQueue();
nodeQueue.add(1);
nodeQueue.poll();
nodeQueue.add(2);
nodeQueue.add(3);
nodeQueue.add(4);
while(!nodeQueue.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(nodeQueue.poll());
}
}
}
결과는 다음과 같다.

반응형
'Java > 개념정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 자바 package (0) | 2021.09.28 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 상속 (2) | 2021.09.27 |
| [Java] Stack (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| [ Java ] LinkedList (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| [Java] 데이터 타입, 변수, 배열 (0) | 2021.09.19 |
댓글
